Extraperitoneal structures
Characteristics:
- Not visible/accessible after opening the peritoneal cavity
- Immobile - embedded in connective tissue
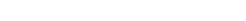 Extraperitoneal: retroperitoneal, subperitoneal, preperitoneal
Extraperitoneal: retroperitoneal, subperitoneal, preperitoneal
By O.P. (Paul) Gobée, dept. of Anatomy and Embryology, Leiden University Medical Center, last update: 17 feb 2018
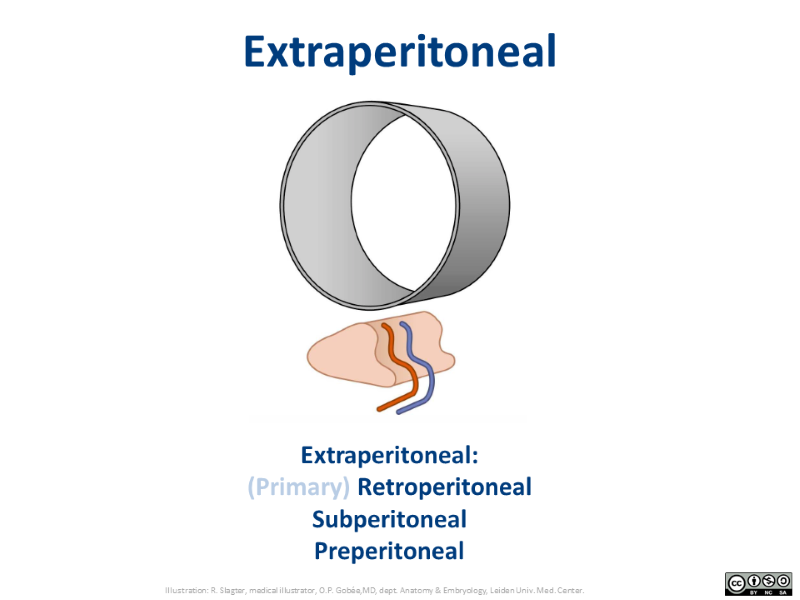
Extraperitoneal is the generic concept that comprises the more commonly used terms for the specific locations: retroperitoneal (posterior to the peritonal cavity), subperitoneal (inferior to the peritonal cavity) and preperitoneal (anterior to the peritonal cavity).
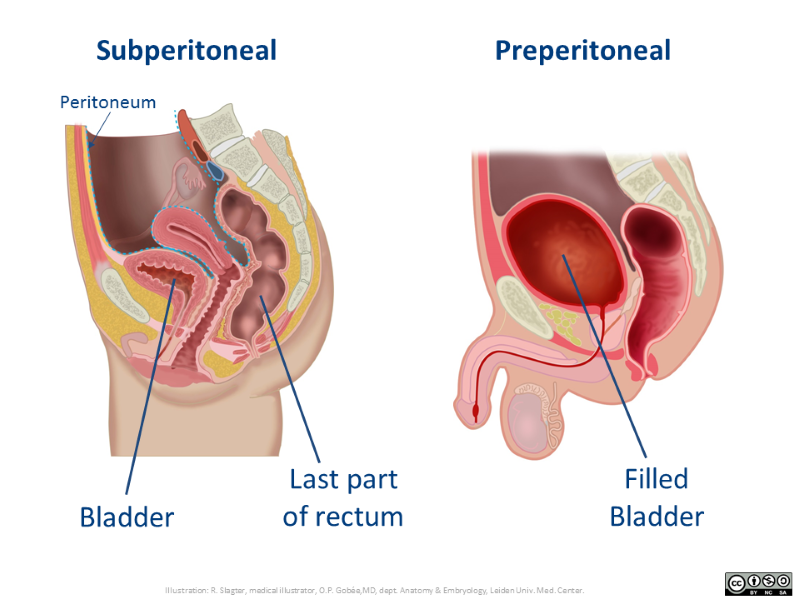
To access extraperitoneal organs, the surgeon can either take a route remaining completely outside or the peritoneal cavity, or traverse the peritoneal cavity, that is: cut the front wall parietal peritoneum to enter the peritoneal cavity and then cut the back wall, or inferior wall parietal peritoneum to reach respectively retroperitoneal or subperitoneal locations.
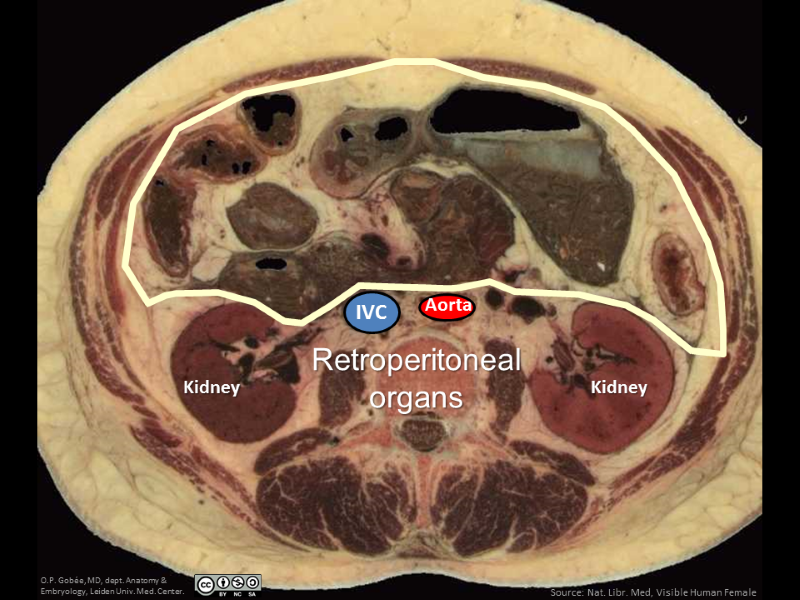
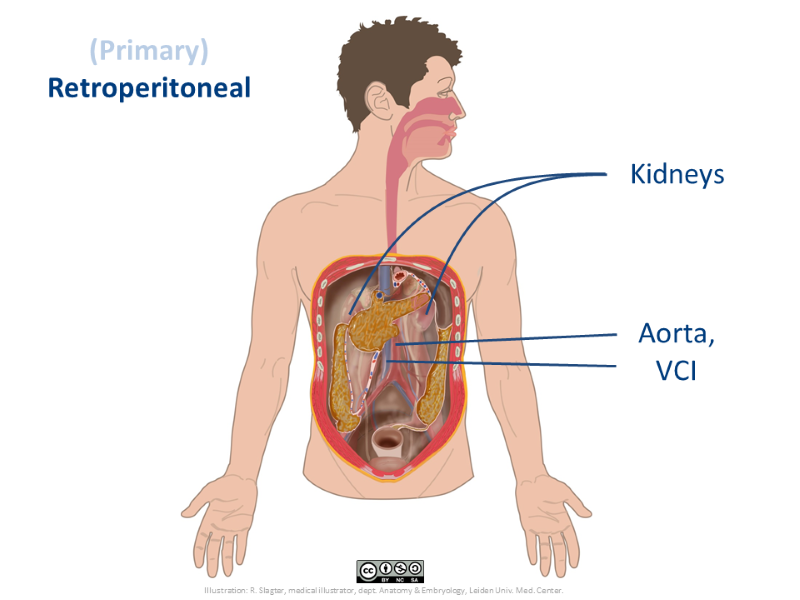
In this video you see the location of (primary) retroperitoneal structures in a dissection specimen. You will notice that they are not visible and not directly accessible, after opening the peritoneal cavity.
This is a fragment of a longer video that shows all three peritoneal locations. See minutes 2:46 - 4:00
(1m14s) 
Characteristics:
 View license
View license If you use this item you should credit it as follows:

Comments