nid: 61522
Additional formats:
None available
Description:
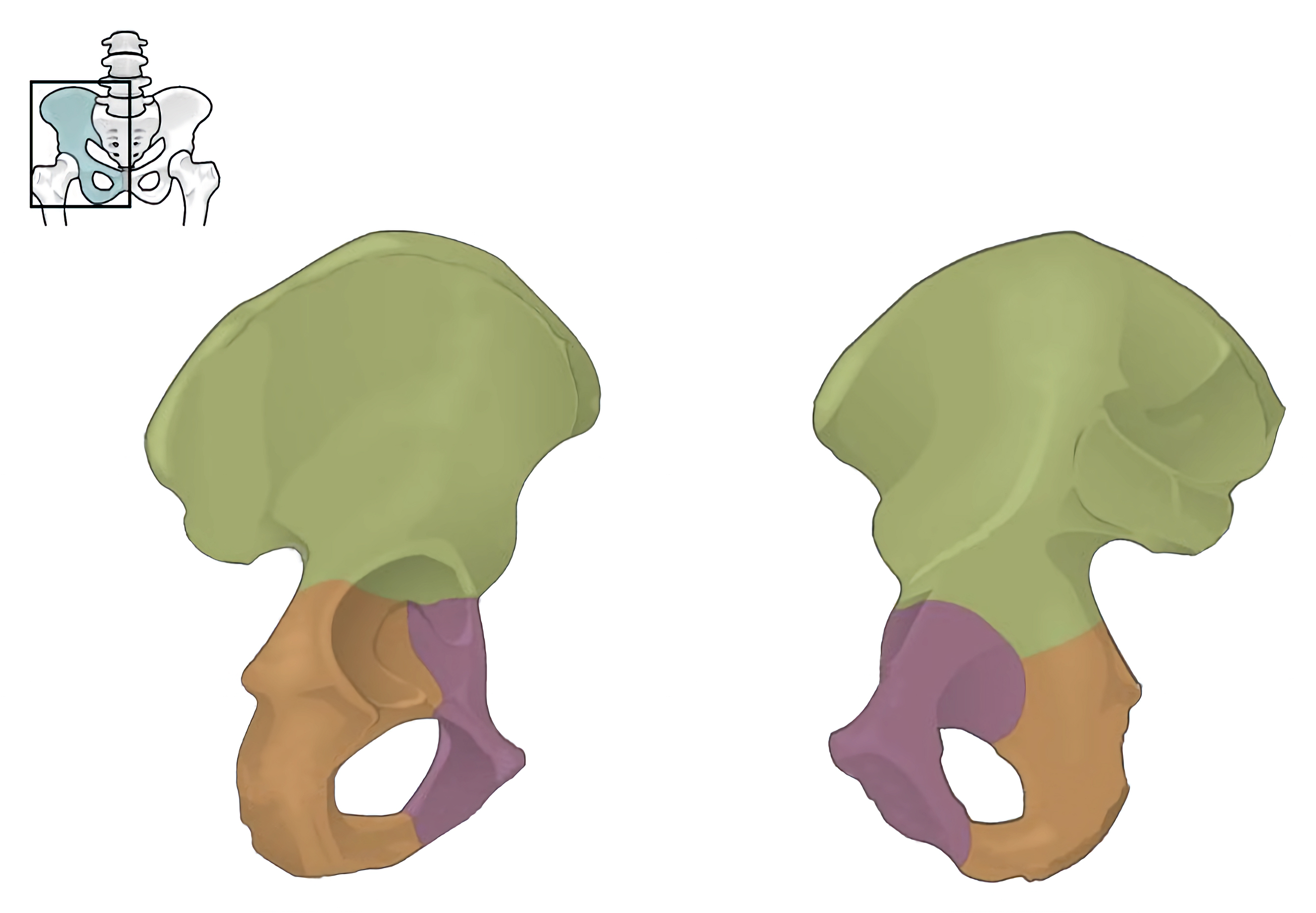
The Hip Bone. The adult hip bone consists of three regions. The ilium forms the large, fan-shaped superior portion, the ischium forms the posteroinferior portion, and the pubis forms the anteromedial portion.
From OpenStax book 'Anatomy and Physiology', fig. 8.13.
Labels removed and colour edited by Marco de Marco, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, AMC.
From OpenStax book 'Anatomy and Physiology', fig. 8.13.
Labels removed and colour edited by Marco de Marco, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, AMC.
Anatomical structures in item:
Uploaded by: rva
Netherlands, Leiden – Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden University
Os coxae
Spina iliaca posterior superior
Spina iliaca posterior inferior
Incisura ischiadica major
Corpus ossis ischii
Spina ischiadica
Ischium
Foramen obturatum
Tuber ischiadicum
Ramusi ossis ischii
Ramus ischiopubicus
Ramus inferior ossis pubis
Pubis
Corpus ossis pubis
Tuberculum pubicum
Ramus superior ossis pubis
Arcuate line of hip bone
Acetabulum
Spina iliaca anterior inferior
Spina iliaca anterior superior
Crista iliaca
Ilium
Fossa iliaca
Facies auricularis ossis ilii
Pelvis
Creator(s)/credit: OpenStax; Marco de Marco, software-engineer, image editing, AMC
Requirements for usage
You are free to use this item if you follow the requirements of the license:  View license
View license
 View license
View license If you use this item you should credit it as follows:
- For usage in print - copy and paste the line below:
- For digital usage (e.g. in PowerPoint, Impress, Word, Writer) - copy and paste the line below (optionally add the license icon):
"OpenStax AnatPhys fig.8.13 - Hip Bone - no labels" at AnatomyTOOL.org by OpenStax and Marco de Marco, AMC, license: Creative Commons Attribution. Source: book 'Anatomy and Physiology', https://openstax.org/details/books/anatomy-and-physiology.
"OpenStax AnatPhys fig.8.13 - Hip Bone - no labels" by OpenStax and Marco de Marco, AMC, license: CC BY. Source: book 'Anatomy and Physiology', https://openstax.org/details/books/anatomy-and-physiology.



Comments