nid: 58688
Additional formats:
None available
Description:
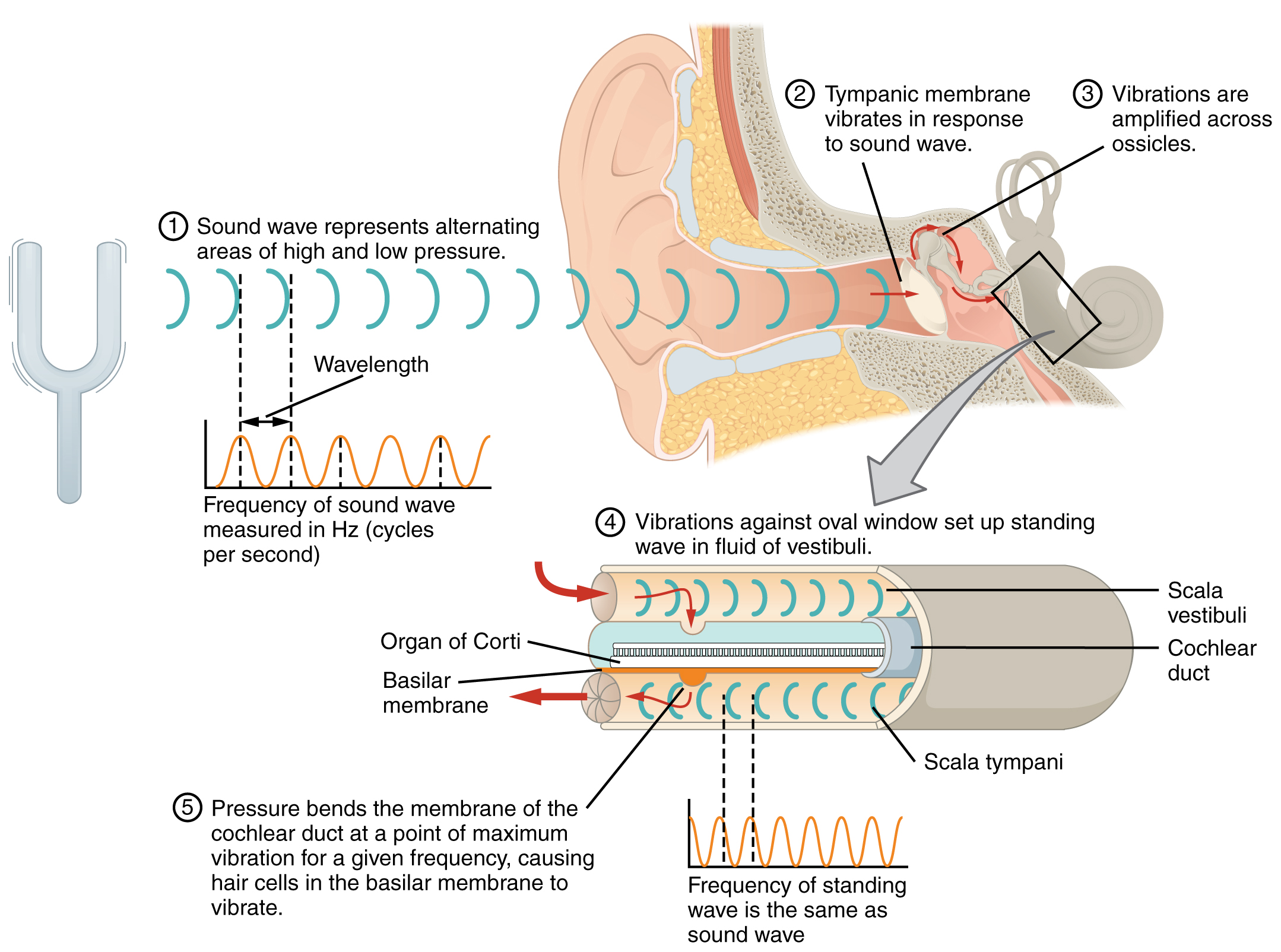
Transmission of Sound Waves to Cochlea. A sound wave causes the tympanic membrane to vibrate. This vibration is amplified as it moves across the malleus, incus, and stapes. The amplified vibration is picked up by the oval window causing pressure waves in the fluid of the scala vestibuli and scala tympani. The complexity of the pressure waves is determined by the changes in amplitude and frequency of the sound waves entering the ear. English labels. From OpenStax book 'Anatomy and Physiology', fig. 14.6.
Anatomical structures in item:
Uploaded by: Jorn IJkhout
Netherlands, Leiden – Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden University
Auris
Cochlea
Organum spirale
Lamina basilaris ductus cochlearis
Scala vestibuli
Ductus cochlearis
Scala tympani
Creator(s)/credit: OpenStax
Requirements for usage
You are free to use this item if you follow the requirements of the license:  View license
View license
 View license
View license If you use this item you should credit it as follows:
- For usage in print - copy and paste the line below:
- For digital usage (e.g. in PowerPoint, Impress, Word, Writer) - copy and paste the line below (optionally add the license icon):
"OpenStax AnatPhys fig.14.6 - Sound Waves and the Ear - English labels" at AnatomyTOOL.org by OpenStax, license: Creative Commons Attribution. Source: book 'Anatomy and Physiology', https://openstax.org/details/books/anatomy-and-physiology.
"OpenStax AnatPhys fig.14.6 - Sound Waves and the Ear - English labels" by OpenStax, license: CC BY. Source: book 'Anatomy and Physiology', https://openstax.org/details/books/anatomy-and-physiology.



Comments