nid: 63584
Additional formats:
None available
Description:
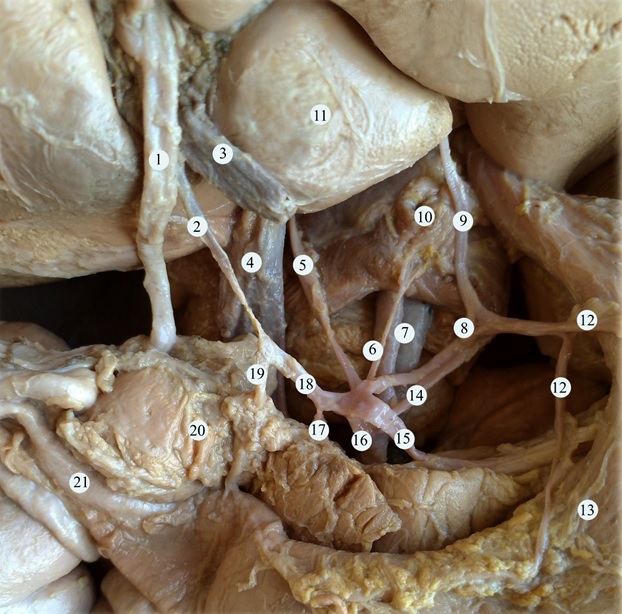
Anatomy of the celiac trunk.
Abstract: we describe a case of unusual development of the celiac trunk observed in the cadaver of 1-year old male child. The celiac trunk branched into five vessels: the splenic, common hepatic and left gastric arteries, the left inferior diaphragmatic artery, and a short trunk that branched into the right inferior diaphragmatic artery and right accessory hepatic artery. Additionally, the manner of branching of the vessel was unusual: it was possible to distinguish two branching points that corresponded to its s-shaped trajectory. There were also other variations of vascular supply, such as the presence of a left accessory hepatic artery, an additional superior pancreatoduodenal artery, and others. It should be noted that multiple developmental variations can be common in clinical practice and clinicians should be aware of them during diagnostic and interventional procedures.
(1) common bile duct; (2) proper hepatic artery; (3) portal vein; (4) inferior vena cava; (5) accessory right hepatic artery; (6) right inferior diaphragmatic artery; (7) abdominal aorta; (8) left gastric artery; (9) left accessory liver artery; (10) the diaphragm; (11) the caudate lobe of the liver; (12) arteries of the lesser curvature of the stomach; (13) stomach; (14) the inferior diaphragmatic artery; (15) splenic artery; (16) celiac trunk; (17) additional superior pancreatoduodenal artery; (18) common hepatic artery; (19) gastroduodenal artery; (20) pancreas; (21) duodenum. Number labels.
Image, abstract and description derived from Covantev S, Mazuruc N, Drangoi I, Belic O. Unusual development of the celiac trunk and its clinical significance J Vasc Bras . 20:2021;e20200032, licenced under Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY).
Abstract: we describe a case of unusual development of the celiac trunk observed in the cadaver of 1-year old male child. The celiac trunk branched into five vessels: the splenic, common hepatic and left gastric arteries, the left inferior diaphragmatic artery, and a short trunk that branched into the right inferior diaphragmatic artery and right accessory hepatic artery. Additionally, the manner of branching of the vessel was unusual: it was possible to distinguish two branching points that corresponded to its s-shaped trajectory. There were also other variations of vascular supply, such as the presence of a left accessory hepatic artery, an additional superior pancreatoduodenal artery, and others. It should be noted that multiple developmental variations can be common in clinical practice and clinicians should be aware of them during diagnostic and interventional procedures.
(1) common bile duct; (2) proper hepatic artery; (3) portal vein; (4) inferior vena cava; (5) accessory right hepatic artery; (6) right inferior diaphragmatic artery; (7) abdominal aorta; (8) left gastric artery; (9) left accessory liver artery; (10) the diaphragm; (11) the caudate lobe of the liver; (12) arteries of the lesser curvature of the stomach; (13) stomach; (14) the inferior diaphragmatic artery; (15) splenic artery; (16) celiac trunk; (17) additional superior pancreatoduodenal artery; (18) common hepatic artery; (19) gastroduodenal artery; (20) pancreas; (21) duodenum. Number labels.
Image, abstract and description derived from Covantev S, Mazuruc N, Drangoi I, Belic O. Unusual development of the celiac trunk and its clinical significance J Vasc Bras . 20:2021;e20200032, licenced under Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY).
Anatomical structures in item:
Uploaded by: rva
Netherlands, Leiden – Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden University
Ductus biliaris
Arteria hepatica propria
Vena portae hepatis
Vena cava inferior
Aorta abdominalis
Arteria gastrica sinistra
Diaphragma
Lobus caudatus hepatis
Ventriculus
Arteria lienalis
Truncus coeliacus
Arteria hepatica communis
Arteria gastroduodenalis
Pancreas
Duodenum
Creator(s)/credit: Serghei D. Covantev MD, surgeon; Natalia Mazuruc, USMF; Irina Drangoi, USMF; Olga Belic, USMF
Requirements for usage
You are free to use this item if you follow the requirements of the license:  View license
View license
 View license
View license If you use this item you should credit it as follows:
- For usage in print - copy and paste the line below:
- For digital usage (e.g. in PowerPoint, Impress, Word, Writer) - copy and paste the line below (optionally add the license icon):
"Covantev et al - Dissection Photo Anatomy of the celiac trunk - number labels" at AnatomyTOOL.org by Serghei D. Covantev, Natalia Mazuruc, USMF, Irina Drangoi, USMF et al, license: Creative Commons Attribution
"Covantev et al - Dissection Photo Anatomy of the celiac trunk - number labels" by Serghei D. Covantev, Natalia Mazuruc, USMF, Irina Drangoi, USMF et al, license: CC BY



Comments