nid: 60391
Additional formats:
None available
Description:
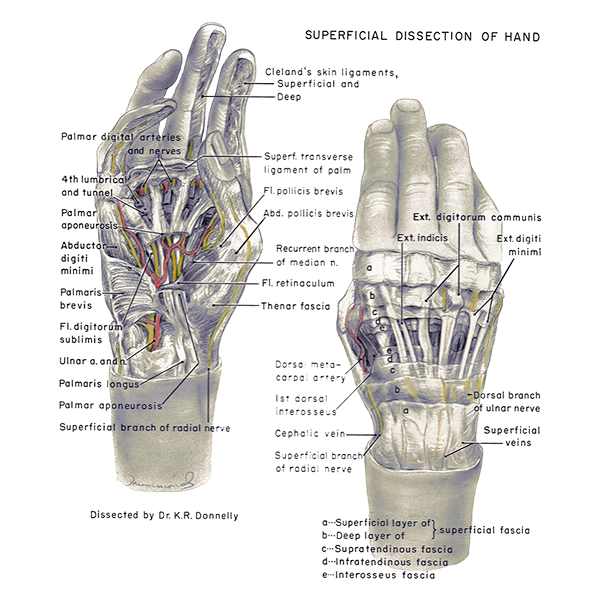
Superficial anatomy of handpalm and dorsum. The nerves and vessels of the palm of the hand can be seen. English labels.
Retrieved from website Clinical Anatomy of the University of British Columbia.
Retrieved from website Clinical Anatomy of the University of British Columbia.
Anatomical structures in item:
Uploaded by: rva
Netherlands, Leiden – Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden University
Manus
Aponeurosis palmaris
Abductor digiti minimi of hand
Musculus palmaris brevis
Musculus flexor digitorum superficialis
Nervus ulnaris
Arteria ulnaris
Eminentia thenaris
Musculus extensor indicis
Musculus extensor digitorum
Musculus extensor digiti minimi
Ramus dorsalis nervus ulnaris
Venae superficiales membri superioris
Tela subcutanea
Creator(s)/credit: Department of Anatomy, University of British Columbia, UBC; Dr. K.R. Donnelly, UBC
Requirements for usage
You are free to use this item if you follow the requirements of the license:  View license
View license
 View license
View license If you use this item you should credit it as follows:
- For usage in print - copy and paste the line below:
- For digital usage (e.g. in PowerPoint, Impress, Word, Writer) - copy and paste the line below (optionally add the license icon):
"U.Br.Columbia - Drawing Superficial anatomy of handpalm and dorsum - English labels" at AnatomyTOOL.org by Department of Anatomy, University of British Columbia, UBC and K.R. Donnelly, UBC, license: Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike. Created for: Department of Anatomy (now Department of Cellular and Physiological Sciences) at the University of British Columbia. Source: website Clinical Anatomy, http://www.clinicalanatomy.ca
"U.Br.Columbia - Drawing Superficial anatomy of handpalm and dorsum - English labels" by Department of Anatomy, University of British Columbia, UBC and K.R. Donnelly, UBC, license: CC BY-NC-SA. Created for: Department of Anatomy (now Department of Cellular and Physiological Sciences) at the University of British Columbia. Source: website Clinical Anatomy, http://www.clinicalanatomy.ca



Comments