nid: 58811
Additional formats:
None available
Description:
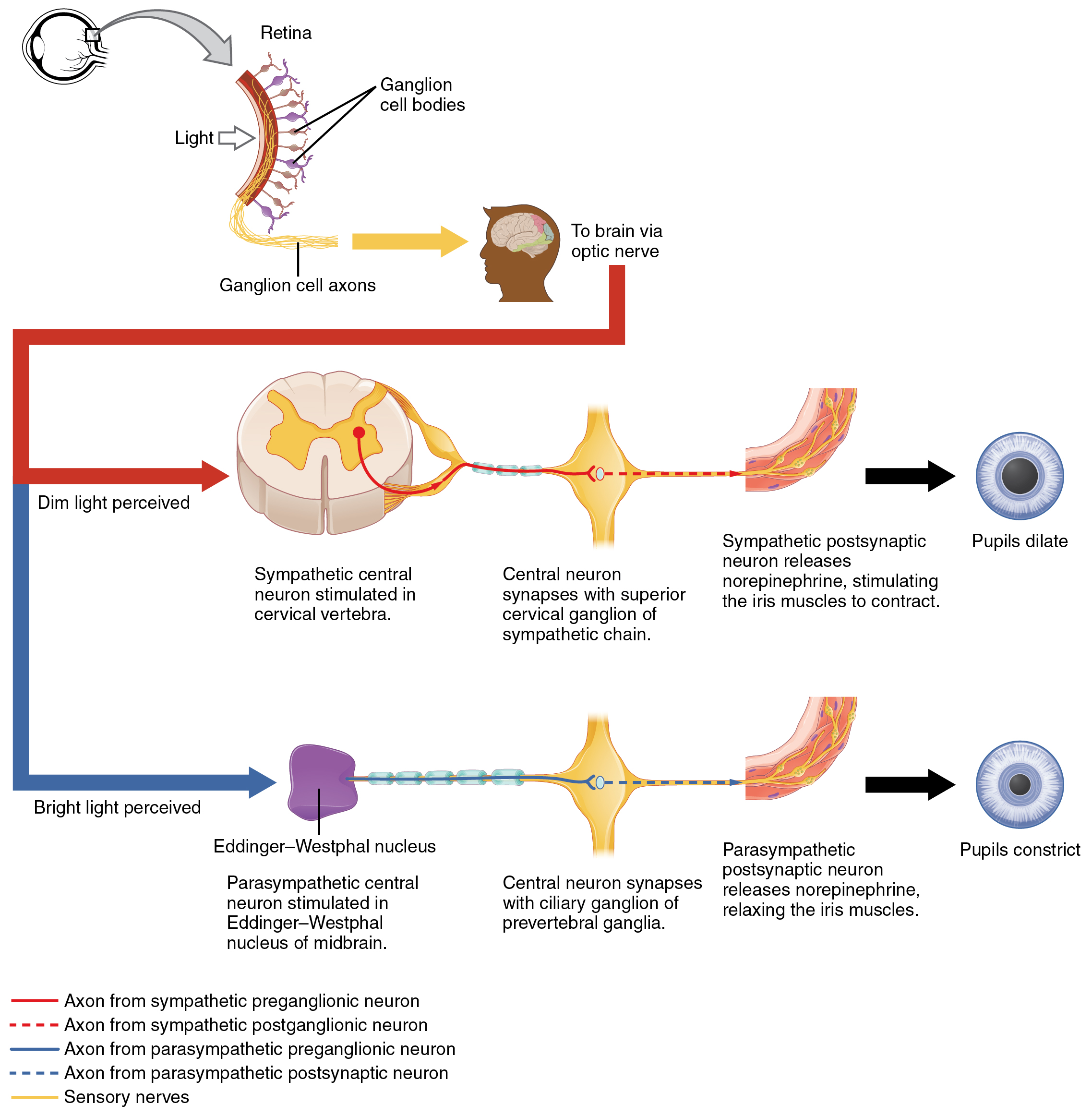
Autonomic Control of Pupillary Size Activation of the pupillary reflex comes from the amount of light activating the retinal ganglion cells, as sent along the optic nerve. The output of the sympathetic system projects through the superior cervical ganglion, where as the parasympathetic system originates out of the midbrain and projects through the oculomotor nerve to the ciliary ganglion, which then projects to the iris. The postganglionic fibers of either division release neurotransmitters onto the smooth muscles of the iris to cause changes in the pupillary size. Norepinephrine results in dilation and ACh results in constriction. English labels. From OpenStax book 'Anatomy and Physiology', fig. 15.9.
Anatomical structures in item:
Uploaded by: Jorn IJkhout
Netherlands, Leiden – Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden University
Nervus
Pupilla
Nervus opticus
Medulla spinalis
Ganglion cervicale superius
Ganglion ciliare
Creator(s)/credit: OpenStax
Requirements for usage
You are free to use this item if you follow the requirements of the license:  View license
View license
 View license
View license If you use this item you should credit it as follows:
- For usage in print - copy and paste the line below:
- For digital usage (e.g. in PowerPoint, Impress, Word, Writer) - copy and paste the line below (optionally add the license icon):
"OpenStax AnatPhys fig.15.9 - Autonomic Control of Pupil Size - English labels" at AnatomyTOOL.org by OpenStax, license: Creative Commons Attribution. Source: book 'Anatomy and Physiology', https://openstax.org/details/books/anatomy-and-physiology.
"OpenStax AnatPhys fig.15.9 - Autonomic Control of Pupil Size - English labels" by OpenStax, license: CC BY. Source: book 'Anatomy and Physiology', https://openstax.org/details/books/anatomy-and-physiology.



Comments